How to Identify and Defeat Two Common Cyberattacks
By Keith Carey | Published January 2025 | ±2 minute Read Time
The Ground Work
Short on time? Here are this article’s key takeaways…
Phishing manipulates victims through emails or messages to share sensitive information, while spoofing deceives by impersonating trusted entities, such as email addresses, phone numbers, or websites.
Aster Brands producer partners have been targeted by fraudsters on several occasions impersonating Aster Brands team members and requesting payment for fake invoices.
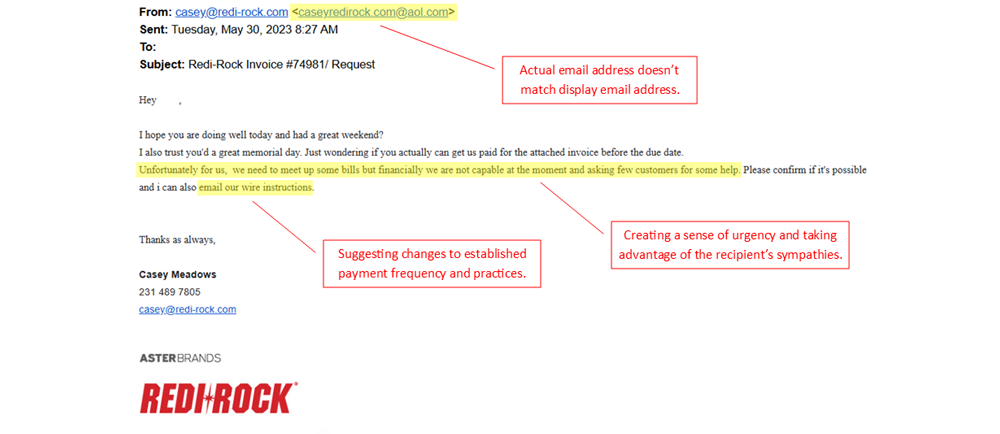
Look out for red flags like generic greetings, spelling errors, suspicious URLs, urgent language, and unexpected attachments in emails or messages.
Combat phishing and spoofing by educating yourself, using email filters, verifying suspicious communications, inspecting links and sender details, keeping software updated, and reporting suspicious activities. Always verify communications before taking action.
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyberattack is a deliberate attempt by an individual or organization to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information, systems, or networks. It typically involves exploiting vulnerabilities or using malicious methods to disrupt operations, steal data or funds, or simply cause damage. This article will address two of the most common cyberattacks within the manufacturing sector – phishing and spoofing.
Why Should Aster Brands Producer-Partners Care?
Over the last year we were made aware of several instances when a fraudster impersonated an Aster Brands team member through email. In these scenarios, the criminal attempted to arrange payment for Aster Brands invoices to bank accounts that were not Aster Brands accounts.
Defining Phishing and Spoofing
Phishing and spoofing are cyberattacks perpetrated through email or messaging. Both involve tricking the recipient into taking action or divulging information the attacker can use for monetary gain but feature slightly different tactics.
Phishing occurs when criminals use email or messaging to manipulate a target into sharing information like usernames, passwords, login credentials, Social Security numbers, and other sensitive data. The emails or messages urge recipients to click malicious links or download harmful attachments.
Spoofing is a type of cyberattack that involves assuming the identity of a trusted entity to manipulate or deceive the recipient. This can include email spoofing (faking the sender’s email address), caller ID spoofing (altering phone numbers), or website spoofing (creating lookalike sites to steal credentials).
Both types of attacks often use scare tactics or a sense of urgency to drive the target to hasty action. The attackers may also attempt to elicit sympathy by describing challenging circumstances that only the recipient can help resolve.
How to Identify Phishing and Spoofing Attempts
Cybercriminals are getting smarter and their tactics more sophisticated, but phishing and spoofing attempts still often include signs that they’re not legitimate communications. So be wary about emails containing:
- Generic Greetings. Legitimate organizations typically address you by name, while phishing emails may use vague terms like “Dear Customer.”
- Spelling and Grammar Errors. Many phishing messages contain typos or awkward phrasing.
- URLs and Links. Hover over links to see the actual URL. Legitimate websites often have secure protocols (https://) and recognizable domain names.
- Urgent Language. Scammers often use urgency or fear tactics, such as claiming your account will be locked, or a bill will be past due unless you act immediately.
- Attachments. Avoid opening unexpected attachments, as they could contain malware.
How to Defeat Phishing and Spoofing Attempts
With cyberattacks increasing and showing no signs of slowing down, chances are you’ll be the target of one soon if you haven’t already. You can utilize a combination of preventive measures and a healthy dose of caution to ensure you or your company don’t fall prey to a phishing or spoofing effort. Consider doing the following to safeguard your communications channels:
- Educate Yourself and Your Team. Awareness is your first line of defense. Regular training on phishing and spoofing tactics can help individuals recognize and avoid attacks.
- Use Email Filters and Security Tools. Advanced email filters can detect and block many phishing attempts. Security software can also prevent malicious links or attachments from causing harm.
- Verify Communications. If you receive an unexpected message from a trusted source, verify its legitimacy through official channels before responding.
- Inspect URLs and Sender Information. Be cautious with messages that request sensitive information or direct you to unfamiliar websites. Double-check email domains and website addresses. Don’t click links without hovering over them and verifying their legitimacy.
- Keep Software Updated. Ensure your devices and applications are up-to-date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Report Suspicious Activity. Most organizations and email providers have mechanisms for reporting phishing attempts. Prompt reporting helps protect others from similar attacks.
Phishing and spoofing remain pervasive threats, but awareness and proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk. You can safeguard your personal and organizational security by staying vigilant, educating yourself, and leveraging security technology. Remember: when in doubt, verify before you trust.

Contributing Expert
Keith Carey
Keith joined the Aster Brands Marketing team in 2022 as a content marketer. He now serves as the team’s content lead, helping to plot the editorial direction for Aster Brands and its five companies. Keith’s professional background includes stints in public policy, small business lobbying, economic development, and financial services marketing. He enjoys coaching high school sports, playing (bad) golf, and embarrassing his two children with impeccably-timed dad jokes.